Big-Bang vs Phased ERP Go-Live: Which Is Right for Your SMB?
Phased vs. big-bang ERP go-live strategies for SMBs. Learn pros, cons, technical risks, and how to choose the right rollout method for your business success.
-
1️⃣What Is Big-Bang ERP Go-Live?
📘 Definition and Core Concept
Big-bang ERP go-live refers to a full-system launch approach in which the new ERP system is switched on across all business units, functions, and users simultaneously on a set date. From that moment, all legacy systems are decommissioned, and business operations are conducted solely through the new ERP platform.
This is an “all-in” approach where planning, configuration, migration, testing, and training are all completed beforehand, and once the system is live, there is no fallback to old software.
⚙️ Technical Prerequisites
For a successful big-bang rollout, several technical conditions must be met:
-
Fully mapped legacy data must be cleansed, validated, and migrated completely.
-
All modules (e.g., finance, inventory, HR, sales) must be configured, integrated, and thoroughly tested.
-
The ERP should be 100% stable, with no critical bugs or unresolved performance issues.
-
All interfaces with external systems (CRM, payroll, e-commerce platforms, etc.) must be finalized and tested under production-like conditions.
-
A robust rollback or failover plan must be in place in case the go-live encounters catastrophic failure.
-
All users must be fully trained and support teams staffed and ready (often 24/7) for the go-live period.
✅ Key Advantages
-
Faster Time-to-Value: The business begins realizing ERP benefits immediately, across all units.
-
Cleaner Data Transition: There's a clear break from legacy systems, reducing data duplication or drift.
-
No Dual-System Complexity: Avoids the need to run and reconcile two systems during the transition period.
-
Streamlined Change Management: Organizational focus is unified around one major event.
⚠️ Main Challenges
-
High Technical and Operational Risk: Any post-go-live bug, misconfiguration, or data issue affects the entire organization at once.
-
Immense Pressure on the Go-Live Day: Even minor oversights can snowball into business disruption.
-
No Real-Time Learning Curve: Users must be fully trained before go-live; there’s no margin for slow adoption.
-
Minimal Room for Phased Correction: Fixes often require real-time patching in a live environment, which can be risky and resource-intensive.
🏢 Ideal Business Profiles for This Strategy
Big-bang ERP go-live is most suitable for:
-
SMBs with simpler business processes and limited geographic/functional complexity.
-
Companies with short ERP module lists (e.g., just finance and inventory).
-
Organizations with strong internal IT and change management capabilities.
-
Businesses undergoing a merger, acquisition, or complete rebranding, where legacy systems must be sunset immediately.
-
Scenarios where the cost of dual operations is unsustainable.
-
-
2️⃣What Is Phased ERP Go-Live?
📘 Definition and Deployment Methods
Phased ERP go-live is a gradual rollout strategy where the ERP system is implemented in stages over time — by module, department, geography, or business unit. Unlike big-bang, the legacy system continues to operate in parallel during the transition, until the entire ERP suite is fully adopted.
Common phased rollout patterns include:
-
Module-by-module (e.g., go live with finance first, then inventory, then HR)
-
Department-by-department (e.g., accounting, then operations)
-
Location-by-location (e.g., start with HQ, then branches)
-
Hybrid (combining any of the above)
⚙️ Technical Requirements
Phased deployment requires strong architectural planning, especially regarding data consistency, interoperability, and user access control. Key technical needs include:
-
Middleware or integration layer to sync data between legacy and ERP systems during overlap
-
Clearly defined cutover criteria per phase
-
Role-based access policies across platforms to prevent duplication
-
Logging and audit trails to monitor cross-system transactions
-
A test environment that mirrors both legacy and ERP co-existence
✅ Key Advantages
-
Reduced Operational Risk: Issues in one phase are contained and can be resolved before expanding.
-
Easier User Adoption: Teams get more time to learn the new system incrementally.
-
More Time for Testing & Feedback: Each module or unit is tested in real-world use before full rollout.
-
Improved Flexibility: Businesses can pause, adjust, or accelerate rollout based on live performance.
⚠️ Main Challenges
-
Complex Data Synchronization: Dual systems must remain in sync without data loss or conflicts.
-
Prolonged Project Timeline: Full implementation can take months or even years.
-
Higher Cumulative Cost: More resource hours, vendor time, and ongoing system reconciliation may increase total costs.
-
Cross-System Training Required: Users may have to toggle between legacy and new systems temporarily.
🏢 Ideal Business Profiles for Phased Rollout
Phased ERP go-live is typically better suited for:
-
Larger SMBs with diverse departments or multiple sites
-
Businesses with mission-critical operations that can’t tolerate even brief downtime
-
Organizations that lack deep technical readiness or internal ERP experience
-
Teams seeking to build ERP competence gradually
-
Firms where some departments are more digitally mature than others
-
-
3️⃣How to Decide: Phased vs. Big-Bang for Your SMB
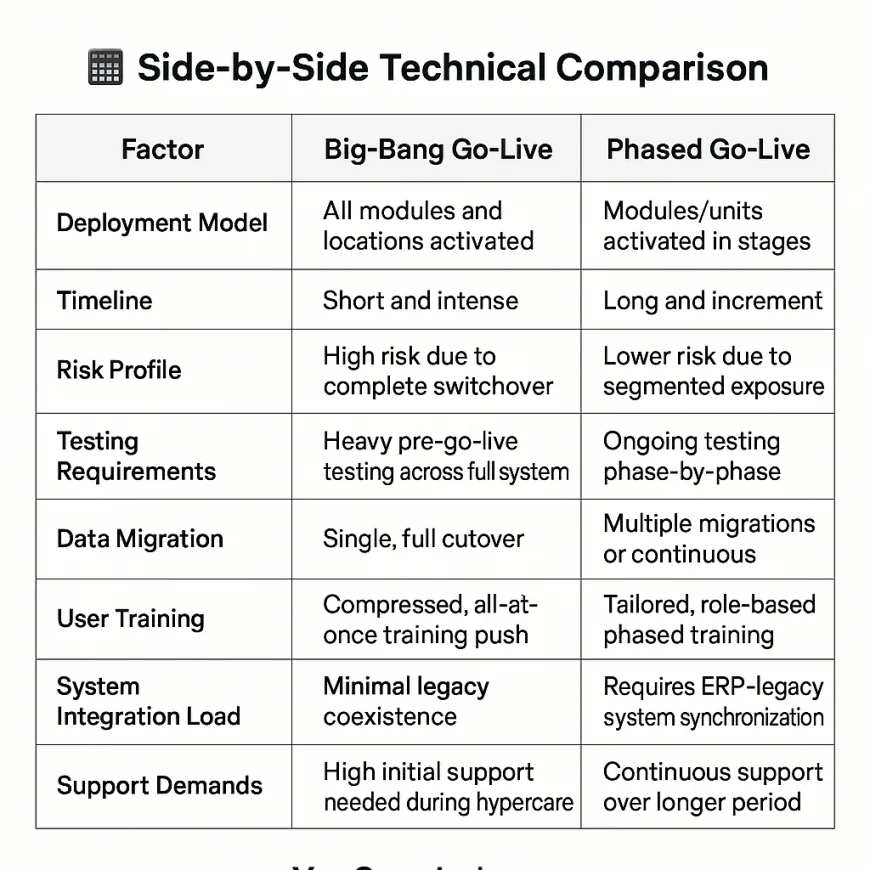
1. Deployment Model
Big-Bang: The entire ERP system, including all modules and departments, goes live simultaneously in one major cutover event.
Phased: The ERP system is rolled out gradually, module by module or department by department, following a planned sequence.
2. Project Timeline
Big-Bang: Shorter overall timeline with an intense period of preparation and launch activities compressed into a single go-live event.
Phased: Longer overall timeline, with each phase allowing for focused deployment, testing, and stabilization before moving on.
3. Risk Exposure
Big-Bang: High risk since any failure impacts the entire organization immediately upon go-live.
Phased: Lower risk because issues are contained within individual phases, reducing business-wide disruption.
4. Testing Requirements
Big-Bang: Requires exhaustive, end-to-end testing of the full system before go-live, including integration and user acceptance testing across all modules.
Phased: Testing is done in stages, corresponding to each phase, allowing for continuous refinement and issue resolution.
5. Data Migration
Big-Bang: All legacy data is cleansed, mapped, and migrated in one single cutover window.
Phased: Data migration occurs incrementally or with data synchronization between legacy and ERP systems during the phased rollout.
6. User Training
Big-Bang: All users must be trained prior to the go-live event, requiring a comprehensive and coordinated training program across the organization.
Phased: Training is delivered progressively, tailored to each module or department as they go live.
7. Legacy System Coexistence
Big-Bang: Legacy systems are fully retired or replaced at once, eliminating the need for parallel operation.
Phased: Legacy systems often run in parallel during the rollout, requiring synchronization and coexistence strategies.
8. IT Support Demand
Big-Bang: Intense support needed immediately after go-live, often requiring a dedicated hypercare team to manage issues.
Phased: Support efforts are spread out over time, which may reduce immediate pressure but extends the overall support period.
-
4️⃣Hybrid ERP Go-Live Models
🔍 What Is a Hybrid ERP Go-Live Approach?
A hybrid ERP go-live model blends elements of both Big-Bang and Phased strategies. Typically, core modules (such as finance, general ledger, or accounts payable) go live in a Big-Bang fashion across the organization, while other non-core modules (e.g., inventory, HR, manufacturing) are rolled out in phases.
This model allows businesses to balance the speed and cohesion of Big-Bang with the risk management and flexibility of phased deployment. It’s often used by SMBs seeking faster ROI on core functionality without fully exposing the entire business to a single massive cutover event.
⚙️ Technical Example: Financial Core + Phased Operations
A common hybrid model looks like this:
-
Go-Live Phase 1 (Big-Bang):
Launch of core financials across the company — general ledger, accounts receivable/payable, fixed assets, and basic reporting.
• Key Dependencies: Chart of accounts, opening balances, banking interfaces. -
Go-Live Phase 2 (Phased):
Rollout of operational modules like inventory management, CRM integration, production planning, or HR/payroll across teams or regions.
• Includes change management, workflow customization, and training. -
Go-Live Phase 3 (Optimization):
Gradual enablement of automation, advanced analytics, mobile access, and user-specific dashboards.
This allows finance to close books and manage compliance early while other departments adapt to their modules over time.
📈 Pros of Hybrid ERP Go-Live
-
Early ROI on Core Functions
Enables faster financial visibility and compliance reporting while other business functions are still onboarding. -
Controlled Risk
Limits exposure by avoiding full-scale deployment while still delivering essential capabilities quickly. -
Better Resource Allocation
Internal teams can focus on one domain at a time instead of a company-wide push, making training, testing, and support more manageable. -
Improved Change Management
Allows organizations to segment communication, training, and support efforts — easing resistance and boosting adoption rates.
⚠️ Constraints of Hybrid Methods
-
Data Synchronization Complexity
Requires interim solutions to bridge live ERP modules with legacy systems still in use, often involving APIs, data lakes, or middleware. -
Integration Maintenance
Maintaining temporary integrations can increase cost and complexity, especially with third-party systems. -
Extended Support Period
Prolonged deployment means extended vendor support contracts and ongoing change management, potentially straining internal resources. -
Risk of Fragmented Experience
If not carefully coordinated, users may face inconsistencies across departments using ERP and those still on legacy systems.
🧩 Vendor Support Considerations
Not all ERP vendors fully support hybrid go-lives. Ensure your vendor or implementation partner:
-
Has clear module-based licensing and deployment flexibility
-
Offers robust integration and migration tooling
-
Can support interim dual-system data sync and user access controls
-
Provides dedicated rollout frameworks for hybrid implementations
A hybrid strategy only succeeds when your implementation partner has experience in orchestrating staggered rollouts without compromising data integrity or business continuity.
-
-
🔷 YouConclude :Go-Live Readiness Tips
✓ YouConclude
✅ When to Say “Go” vs. “Not Yet”
Before launching any ERP go-live — Big-Bang, Phased, or Hybrid — your team must conduct a formal Go/No-Go review. This is a cross-functional checkpoint where decision-makers evaluate whether all critical systems, users, and data are ready for production.
Say “Go” only if ALL of the following are true:
-
Data migration is fully validated and reconciled
-
End-user training is complete and role-specific
-
Key integrations are tested and functioning
-
Contingency plans (including rollback) are approved
-
Stakeholders have signed off on system and process readiness
-
All critical defects from UAT are resolved or mitigated
Say “Not Yet” if any of the following apply:
-
Major modules are not tested end-to-end
-
Business users are still unclear on new workflows
-
Data mapping or transformation rules are incomplete
-
High-severity defects are still open
-
Support team is not fully staffed or trained for post-launch
Never launch under pressure from executive timelines unless technical and operational readiness are verified.
📌 Critical Assessments Before Launch
Use these readiness gates as part of your final decision framework:
-
Business Readiness
-
Are key process owners confident in their post-launch responsibilities?
-
Is downstream reporting configured for compliance and auditing?
-
-
Technical Infrastructure
-
Is your production environment load-tested and backed up?
-
Are alerting, logging, and failover protocols in place?
-
-
Data Integrity
-
Has the final reconciliation between legacy and ERP been signed off?
-
Are security roles applied consistently across migrated data?
-
-
End-User Preparedness
-
Is a helpdesk and escalation process in place for common issues?
-
Has internal documentation been distributed and reviewed?
-
-
Operational Impact Assessment
-
Will business performance be impacted by cutover? If so, how?
-
Do you have buffer days to handle post-go-live corrections?
-
🛠️ Technical Tools for Go-Live Confidence
Before finalizing your go-live, implement these essential tools:
🔁 Mock Cutovers
Simulate the go-live process from start to finish — including backups, data migration, system startup, and user validation. This ensures timing, sequence, and technical scripts work as expected under realistic conditions.
📋 Cutover Checklist Frameworks
Maintain a detailed, time-stamped checklist for each step of your go-live. Assign responsibilities to individuals for system backups, server provisioning, DNS switching, and initial data verification.
⏮️ Rollback Protocols
Always prepare a rollback plan in case the go-live fails. This should include:
-
Restoration points for all critical systems
-
Communication scripts for notifying users
-
Resource allocation for immediate post-rollback triage
Rollback should be tested just like deployment — not theorized.
Final Thought: Treat ERP Go-Live as a Transition, Not a Destination
Even after a successful go-live, the work is not finished. Invest in hypercare support, conduct a lessons-learned review, and build a continuous improvement roadmap. ERP success depends not just on launch execution, but on post-implementation optimization and user adoption.
-
-
✓ YouConclude More
🔄Construction chaos or controlled execution? The ERP you choose decides.
This list breaks down the top construction ERP platforms, covering field tracking, job costing, and contractor workflows — all ranked to help you build smarter.👉 Best Construction ERP Systems: Top 10 Ranked & Reviewed
🔄 Warehouses don’t run on hope — they run on efficiency, and the right ERP makes all the difference.
This guide ranks the top 10 distribution-focused ERP systems that streamline logistics, reduce delays, and optimize inventory in real time.👉 10 Best Distribution ERP Solutions for Supply Chain Efficiency
🔄 Want powerful ERP without the price tag?
Discover the top free ERP platforms that punch above their weight — including open-source options built to scale, streamline operations, and drive real ROI for lean SMBs.
👉 Best Free ERP Software Options (Ranked + Compared)
🔄 Choosing an ERP system shouldn’t feel like guesswork.
This battle-tested framework walks you through the entire ERP selection process — with clear, confident steps to help you avoid costly missteps and choose with precision.
👉 How to Choose an ERP System: Step-by-Step Guide
🔄 Rolling out ERP? One wrong move can stall your business.
Follow this expert-led roadmap to execute your ERP implementation with confidence — from planning and data migration to user training and go-live optimization.
👉 ERP Implementation Guide for SMBs: Step-by-Step Plan
🔩Choose the Right ERP System to Streamline Your Factory and Scale with Confidence
Discover ERP systems built specifically for manufacturers — with powerful features for shop floor control, inventory accuracy, and production scheduling. Compare usability, pricing, and industry fit in one expert-curated guide.👉The 10 Best Manufacturing ERP Software Tools for Efficiency
🔄 Not sure whether to choose Cloud ERP or stick with On-Premise?
You’re not alone. This guide unpacks the core differences in cost, control, scalability, and security — with detailed insights and real-world comparisons built for IT leaders and growth-focused operations teams.👉 Cloud ERP vs On-Premise: Key Differences Explained
🔄 CRM vs ERP: What’s the Difference & Which Do You Really Need?
Confused between CRM and ERP? You’re not alone. This guide breaks down the real differences, use cases, and ROI impact — with deep analysis and real-world examples designed for operational and growth-focused decision-makers.👉 CRM vs ERP: What’s the Difference & Which Do You Really Need?
🔄 ERP vs MRP: Full Breakdown for Business Decision-Makers
Still torn between ERP and MRP? Learn which system will actually drive results for your operations — with deep comparisons, expert insights, and real-world examples made for serious decision-makers.👉 ERP vs MRP: Full Breakdown for Business Decision-Makers
🔄 What Is ERP? A Complete Guide for SMBs (No Fluff)
Learn everything about ERP systems — how they work, core modules, real-world use cases, benefits, costs, and how to choose the right one for your growing business.👉 Master ERP from A to Z — No Need to Read Another Guide
🔄 The 7 Best ERP Systems for Large Enterprises
Expert-vetted list of powerful ERP platforms built to handle global operations, complex workflows, and enterprise-grade integrations at scale.👉 Discover Which ERP System Powers Leading Enterprises
🔄 The 7 Best ERP Tools for Small & Mid-Sized Businesses
Find easy-to-use, scalable, and affordable ERP platforms made for growing SMBs — with features, pricing, and integrations compared in detail.👉 Choose the Right ERP System to Fuel Your Business Growth
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0